문제점
스프링에서는 인터페이스를 이용하여 Service와 Repository를 구현하곤 한다
여기서 체크예외를 사용했을 때의 문제점은 아래와 같다
1. 예외누수
2. JDBC와 같은 특정 기술에 종속
예외누수
아래와 같은 구조로 Member에 대한 비즈니스 로직을 구현한다고 가정하자
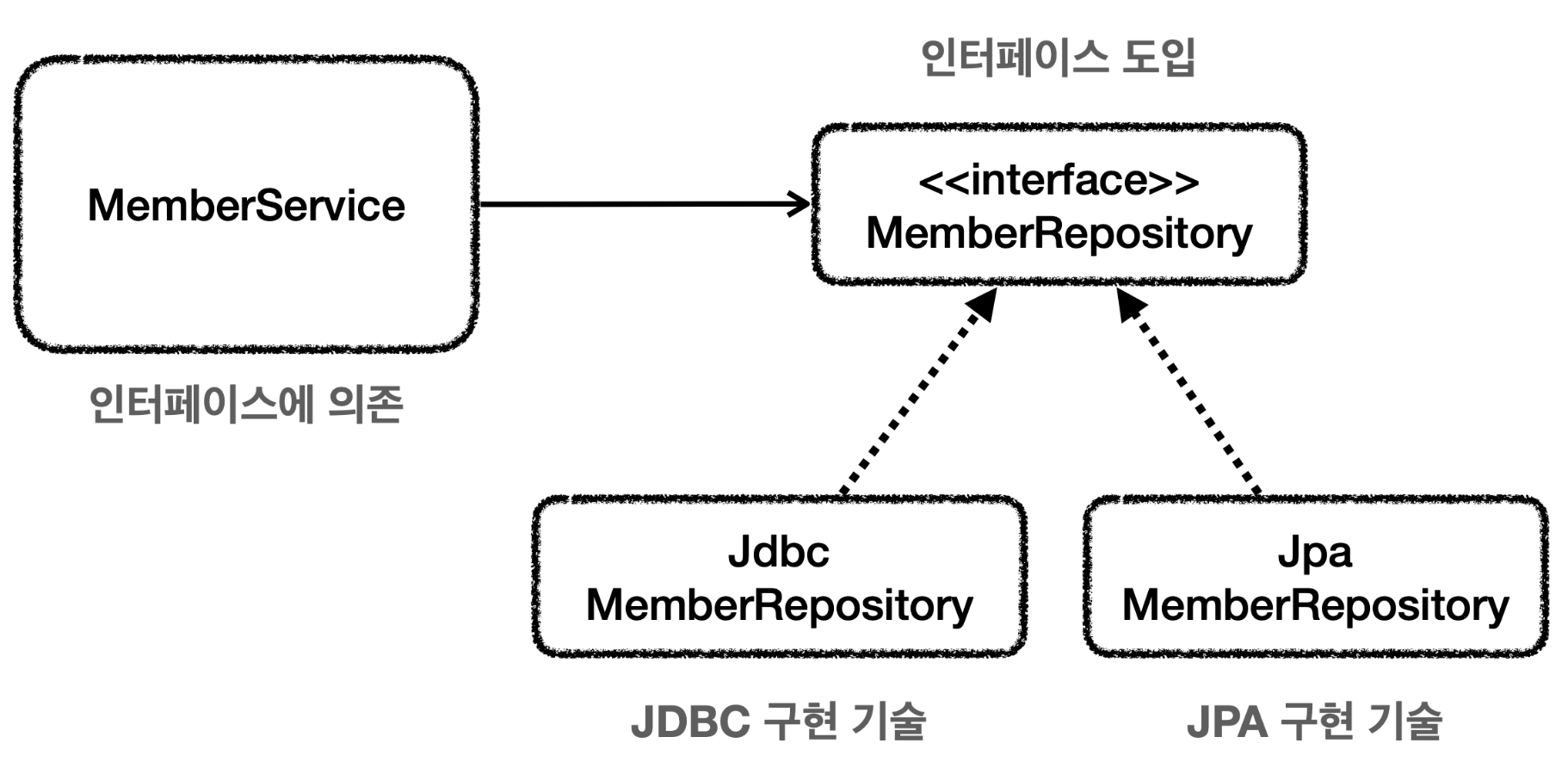
아래는 MemberRepository와 MemberRepository의 구현체 MemberRepositoryImpl의 코드이다
public interface MemberRepository {
Member save(Member member) throws SQLException;
Member findById(String memberId) throws SQLException;
void update(String memberId, int money) throws SQLException;
void delete(String memberId) throws SQLException;
}
public class MemberRepositoryImpl implements MemberRepository {
public Member save(Member member) throws SQLException {
String sql = "insert into member(member_id, money) values(?, ?)";
}
}
JDBC Template을 사용하는 경우를 가정해보자
위 인터페이스는 SQLException이라는 Checked Exception에 의존하고 있다.
인터페이스에 Checked Exception이 명시되어 있으면
해당 인터페이스를 상속한 구현체에서도 인터페이스의 Checked Exception을 명시해야한다.
SQLException은 JDBC Template에서 주로 발생하는 Exception이며, JPA 사용시에는 다른 Exception이 발생할 수 있다.
그러므로, JDBC Template에서 JPA로 기술을 전환할 때, 해당 인터페이스를 구현한 모든 구현체의 소스코드를 수정해야한다.
만약 구현체가 100개라면 100개를 전부 수정해야 한다는 문제가 있다.
또, 상위계층인 Service와 Controller에서도 Checked Exception을 명시해야하는 문제가 있다.
문제 해결
Runtime Exception 적용
Runtime Exception은 Unchecked Exception이라고도 한다.
(이하, Runtime Exception이라고 칭하겠다)
Runtime Exception을 적용하면 위의 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
Runtime Exception은 Exception을 메서드 시그니처에 명시하지 않아도 되기 때문이다.
Checked Exception 발생 시, Runtime Exception으로 변환하기 위해
MyDbException이라는 Runtime Exception을 생성하겠다
public class MyDbException extends RuntimeException {
public MyDbException() {
}
public MyDbException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public MyDbException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public MyDbException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
}
MyDbException의 생성자의 인자에 SQLException을 전달하면 Runtime Exception으로 변환할 수 있다.
아래는 MemberRepositoryImpl에 MyDbException을 적용한 코드이다.
public class MemeberRepositoryImpl implements MemberRepository {
private final DataSource dataSource;
public MemberRepositoryImpl(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
@Override
public Member save(Member member) {
String sql = "INSERT INTO member (member_id, money) VALUES (?, ?)";
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, member.getMemberId());
preparedStatement.setInt(2, member.getMoney());
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
return member;
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new MyDbException(e); //SQLException을 MyDbException으로 변환
} finally {
close(connection, preparedStatement, null );
}
}
@Override
public Member findById(String memberId) {
String sql = "SELECT * FROM member WHERE member_id = ?";
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, memberId);
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
if (resultSet.next()) {
Member member = new Member();
member.setMemberId(resultSet.getString("member_id"));
member.setMoney(resultSet.getInt("money"));
return member;
} else {
throw new NoSuchElementException("member not found memberId=" + memberId);
}
} catch (SQLException e){
throw new MyDbException(e);
} finally {
close(connection, preparedStatement, resultSet);
}
}
@Override
public void update(String memberId, Integer money) {
String sql = "UPDATE member SET money = ? WHERE member_id = ?";
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1, money);
preparedStatement.setString(2, memberId);
int size = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
log.info("update rows = {}", size);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new MyDbException(e);
} finally {
close(connection, preparedStatement, null );
}
}
@Override
public void delete(String memberId) {
String sql = "DELETE FROM member WHERE member_id = ?";
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, memberId);
int size = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
log.info("deleted rows = {}", size);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new MyDbException(e);
} finally {
close(connection, preparedStatement, null );
}
}
private void close(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
JdbcUtils.closeResultSet(resultSet);
JdbcUtils.closeStatement(statement);
// 트랜잭션 동기화를 사용하려면 DataSourceUtils를 사용해야 한다
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(connection, dataSource);
}
private Connection getConnection() {
// 트랜잭션 동기화를 사용하려면 DataSourceUtils를 사용해야 한다
Connection connection = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(dataSource);
log.info("get connection = {}, class = {}", connection, connection.getClass());
return connection;
}
}
위와 같이 SQLException을 MyDbException이라는 Runtime Exception으로 변환함으로써
예외에 대한 의존문제를 해결하였다.
하지만, 한가지 불편한 점이 있다.
예외가 발생했을 때, 예외를 프로그램적으로 처리할 수 없고, 개발자가 로그를 확인해야만 예외의 원인을 알 수 있다.
예외 원인 별 예외 작성
예외 원인 별로 예외를 처리하기 위해
예외 원인에 별로 예외를 작성하려고 한다.
예를 들어서, PK 중복에 대한 예외를 작성해보겠다
해당 예외는 MyDuplicateKeyException이라고 칭하겠다
MyDuplicateKeyException
public class MyDuplicateKeyException extends MyDbException {
public MyDuplicateKeyException() {
}
public MyDuplicateKeyException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public MyDuplicateKeyException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public MyDuplicateKeyException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
}
MemberRepositoryImpl
public class MemberRepositoryImpl implements MemberRepository {
private final DataSource dataSource;
private final SQLExceptionTranslator exTranslator;
public MemberRepositoryImpl(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
this.exTranslator = new SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator(dataSource);
}
@Override
public Member save(Member member) {
String sql = "INSERT INTO member (member_id, money) VALUES (?, ?)";
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, member.getMemberId());
preparedStatement.setInt(2, member.getMoney());
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
return member;
} catch (SQLException e) {
catch (SQLException e) {
//h2 db
// 23505는 PK 중복 시에 H2 DB에서 던지는 에러코드임
if (e.getErrorCode() == 23505) { // PK 중복발생
throw new MyDuplicateKeyException(e); // MyDuplicateKeyException 던짐
}
// 그 외의 경우, MyDbException 던짐
throw new MyDbException(e);
} finally {
close(connection, preparedStatement, null );
}
}
...
private void close(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
JdbcUtils.closeResultSet(resultSet);
JdbcUtils.closeStatement(statement);
// 트랜잭션 동기화를 사용하려면 DataSourceUtils를 사용해야 한다
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(connection, dataSource);
}
private Connection getConnection() {
// 트랜잭션 동기화를 사용하려면 DataSourceUtils를 사용해야 한다
Connection connection = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(dataSource);
log.info("get connection = {}, class = {}", connection, connection.getClass());
return connection;
}
}
SQLExcpetion에서는 DB에서 던지는 에러코드를 포함하고 있다.
위 코드에서는 PK 중복 시에 H2 DB에서 던지는 에러코드인 23505를 이용하여 PK 중복 시 예외를 처리하였다.
위와 같이 처리할 경우, Service 단에서는 PK 중복으로 인한 예외와 다른 예외를 구분할 수 있으므로 아래와 같이 처리할 수 있다.
MemeberService
아래 코드는 MemberService의 내용 중 일부이다.
PK 중복으로 인한 예외와 다른 예외를 구분할 수 있으므로
PK 중복에 대한 예외를 정확하게 처리할 수 있게 되었다.
try {
repository.save(new Member(memberId, 0));
log.info("saveId={}", memberId);
} catch (MyDuplicateKeyException e) {
log.info("키 중복, 복구 시도");
String retryId = generateNewId(memberId); // PK 재생성
log.info("retryId={}", retryId);
repository.save(new Member(retryId, 0));
} catch (MyDbException e) {
log.info("데이터 접근 계층 예외", e);
throw e;
}
다만, 여기서 문제가 있는데
DB에서 던지는 에러코드는 각 DB마다 다르다는 것이다.
예를 들어, PK 중복에 대한 에러코드가 H2에서는 23505이지만, MySQL에서는 1062일 수 있다.
DB 에러코드는 PK 중복 말고도 수많은 경우의 에러코드가 존재한다.
개발자가 모든 에러코드에 대한 예외를 다루기는 어렵다.
그래서 스프링에서는 예외에 대한 추상화를 제공한다.

위 그림처럼 스프링에서는 DB 예외의 최상위 예외인 DataAccessException을 제공한다.
그 하위에서는 일시적인 원인으로 인한 예외와 그렇지 않은 경우에 대한 예외를 제공한다
일시적인 원인에 대한 예외는 TransientDataAccessException으로 처리하고
일지적이지 않은 원인에 대한 예외는 NonTransientDataAccessException으로 처리할 수 있도록 예외를 제공한다.
위와 같이 스프링에서 예외에 대한 추상화를 제공함으로써
특정 기술에 종속된 예외를 사용하지 않아도 되게 되었다.
또한, 기존에 개발자가 DB의 에러코드를 기준으로 예외를 처리해야해서
예외처리 시, DB에 대한 의존성이 있었는데
이러한 문제를 해결하기 위해서 스프링에서는 SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator라는 SQLExceptionTranslator를 제공한다
아래에서 사용 예를 살펴보겠다
SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator 사용 예
SQLExceptionTranslator exTranslator = new SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator(dataSource);
DataAccessException resultEx = exTranslator.translate("select", sql, e);translate() 메서드의 첫번째 파라미터는 읽을 수 있는 설명이고,
두번째는 실행한 sql, 마지막은 발생된 SQLException을 전달하면 된다.
이렇게 하면 적절한 스프링 데이터 접근 계층의 예외로 변환해서 반환해준다.
MemeberRepositoryImpl 적용 예
public class MemeberRepositoryImpl implements MemberRepository {
private final DataSource dataSource;
private final SQLExceptionTranslator exTranslator;
public MemberRepositoryImpl(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
this.exTranslator = new SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator(dataSource);
}
@Override
public Member save(Member member) {
String sql = "INSERT INTO member (member_id, money) VALUES (?, ?)";
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, member.getMemberId());
preparedStatement.setInt(2, member.getMoney());
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
return member;
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw exTranslator.translate("save", sql, e); // Spring에서 제공하는 예외로 변환
} finally {
close(connection, preparedStatement, null );
}
}
...
private void close(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
JdbcUtils.closeResultSet(resultSet);
JdbcUtils.closeStatement(statement);
// 트랜잭션 동기화를 사용하려면 DataSourceUtils를 사용해야 한다
DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(connection, dataSource);
}
private Connection getConnection() {
// 트랜잭션 동기화를 사용하려면 DataSourceUtils를 사용해야 한다
Connection connection = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(dataSource);
log.info("get connection = {}, class = {}", connection, connection.getClass());
return connection;
}
}위 소스코드의 save 메서드에서 SQLException 발생 시,
SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator를 이용하여 스프링에서 제공하는 예외로 변환하고 던지는 모습을 볼 수 있다
그렇다면 스프링은 그 많은 DB들의 에러코드에 대해 예외를 어떻게 변환해줄까?
바로 DB별 에러코드에 대한 예외를 매핑해놓기 때문이다.
스프링에서는 sql-error-codes.xml이라는 파일에 DB별 에러코드에 대해 예외를 매핑해놓았다.
<bean id="H2" class="org.springframework.jdbc.support.SQLErrorCodes">
<property name="badSqlGrammarCodes">
<value>42000,42001,42101,42102,42111,42112,42121,42122,42132</value>
</property>
<property name="duplicateKeyCodes">
<value>23001,23505</value>
</property>
...
</bean>
<bean id="MySQL" class="org.springframework.jdbc.support.SQLErrorCodes">
<property name="databaseProductNames">
<list>
<value>MySQL</value>
<value>MariaDB</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="badSqlGrammarCodes">
<value>1054,1064,1146</value>
</property>
<property name="duplicateKeyCodes">
<value>1062</value>
</property>
...
</bean>스프링은 위의 XML파일을 참조하여 DB별 에러코드에 대해 예외를 변환해준다
이로써 개발자는 기존에 DB에 의존성을 가졌던 예외처리방식을 사용하지 않아도 되게 되었다.
물론, 스프링에서 제공하는 방법이므로 스프링에 기술적으로 의존하지만
개발자가 일일이 예외를 만들고 처리하는 방법은 실용적인 방법이 아니다.
'Spring > Spring DB' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 문제해결 - JDBC 반복 (0) | 2025.07.28 |
|---|---|
| 자바 예외(Exception) (3) | 2025.07.21 |
| 문제해결 - 트랜잭션 동기화 문제 (1) | 2025.07.19 |
| 문제해결 - 트랜잭션 처리 코드 반복 문제 (0) | 2025.07.19 |
| DB Lock (0) | 2025.07.18 |



댓글